Welcome to CS 225!
Welcome to CS 225: Data Structures! In CS 225, you will be using C++ and the Linux operating system to aid your journey in becoming a master of data structures!
Setting Up For CS 225
Before you can begin working on assignments, you will need to set up EWS or your own computer to begin development work. Afterwards, you will need to set up your git repository, your code base you will use to receive mps and labs/submit them for grading.
If you are working on an EWS machine…
Everytime you open a new terminal or ssh session to EWS, you will need to run the following:
module load llvm/6.0.1
If you want to save some hassles of running the above command frequently, you can write it in your .bashrc file. All commands in the .bashrc file will be automatically loaded after opening a new termial. The command below helps you write the “module load llvm/6.0.1” into your .bashrc file in your home directory.
echo 'module load llvm/6.0.1' >> ~/.bashrc
or setup your computer locally
Setup Your Git Repository
Checking Out the Code
From your CS 225 git directory, run the following on EWS or in your VM:
git fetch release
git merge release/lab_intro -m "Merging initial lab_into files"
If you’re on your own machine, you may need to run:
git fetch release
git merge --allow-unrelated-histories release/lab_intro -m "Merging initial lab_into files"
Upon a successful merge, your lab_into files are now in your lab_into directory.
Getting Started
You’ll be using the command line for much of C++. If you’re not comfortable with the command line yet, check out this guide on the command line.
You’ll want to find a text editor you like. Here are some suggestions
Three standard editors that work within a command line interface:
nano, simple and user-friendly for quick editsvim, powerful but very un-friendly to beginnersemacs, powerful but also un-friendly to beginners
Beginner friendly’s with graphical UI’s:
visual studio code, free light-weight editor developed by Microsoft (Our Recommendation)atom, open-source editor developed by github
Lab Insight
This lab is the starting point in your CS 225 class journey. It will touch some of the starting base concepts that will guide you through the class and be your aid in learning about data structures. Hope you have fun throughout the course.
Working With Partners
For your lab assignments (not MPs), you may work with partners! All of you must also submit a working set of code to get credits. Your grade on the lab will depend entirely on the code you submit. You must also understand the code you submit for the assignment and be able to explain it if asked.
Understanding the HSL Color Space
In CS 225, we will not be working with the physical properties of color that you may be familiar with from other sources (the “RGB color space” for red-green-blue channels.) Instead, we will be using an alternative color space that represents colors by human perception of color.
The HSL color space uses the Hue, Saturation, and Luminance of the color. From the Adobe Technical Guides page on “The HSB/HLS Color Model”, Adobe explores these terms:
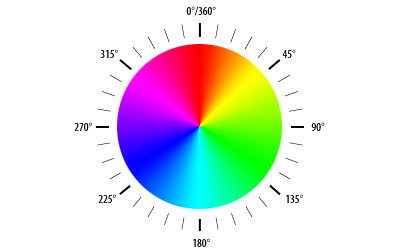
Hue (denoted as h) defines the color itself, for example, red in distinction to blue or yellow. The values for the hue axis run from 0–360° beginning and ending with red and running through green, blue and all intermediary colors like greenish-blue, orange, purple, etc.
There are two hues that we’ll use later in this lab:
- “Illini Orange” has a hue of 11
- “Illini Blue” has a hue of 216

Saturation (denoted as s) indicates the degree to which the hue differs from a neutral gray. The values run from 0%, which is no color saturation, to 100%, which is the fullest saturation of a given hue at a given percentage of illumination.

Luminance (denoted as l) indicates the level of illumination. The values run as percentages; 0% appears black (no light) while 100% is full illumination, which washes out the color (it appears white).
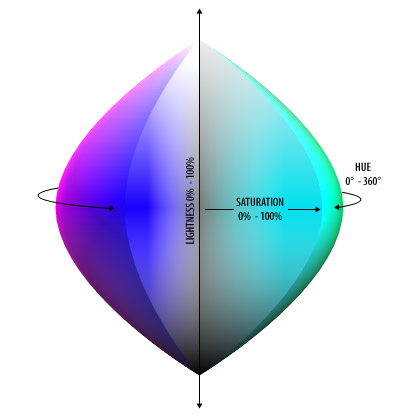
The full HSL color space is a three-dimensional space, but it is not a cube (nor exactly cylindrical). The area truncates towards the two ends of the luminance axis and is widest in the middle range. The ellipsoid reveals several properties of the HSL color space:
- At
l=0orl=1(the top and bottom points of the ellipsoid), the 3D space is a single point (the color black and the color white). Hue and saturation values don’t change the color. - At
s=0(the vertical core of the ellipsoid), the 3D space is a line (the grayscale colors, defined only by the luminance). The values of the hue do not change the color. - At
s=1(the outer shell of the ellipsoid), colors are vivid and dramatic!
Reading your first class: HSLAPixel
Motivation
Before starting on this assignment, be sure to familiarize yourself with the already complete HSLA pixel class that maintains a single HSL pixel. We will use this class a lot throughout CS 225, so let’s use an API that is simple. As reference, here is a simple example of a class.
We’ll refer to this class as an HSLAPixel and place it inside of the cs225 namespace, an organization of data structures that we’ll use commonly within CS 225. Following convention, the definition must be placed in a file called cs225/HSLAPixel.h, and the member function implementations must be placed in a file called cs225/HSLAPixel.cpp.
Specification
The default class HSLAPixel contains four public member variables:
- Let
hdenote the hue of the pixel, storing the value of the hue in degrees as adoublefrom [0, 360). - Let
sdenote the saturation of the pixel, storing the value as adoublefrom [0, 1]. - Let
ldenote the luminance of the pixel, storing the value as adoublefrom [0, 1]. - Let
adenote the alpha channel, how transparent the pixel is, storing the value as adoublefrom [0, 1].
Additionally, there are three constructors defined in the Doxygen:
Compile and Testing
A Makefile has been provided for you for this lab (you’ll make your own soon!). To compile your program, run:
$ make
If make fails, you will see error messages. We use clang, which aims to provides descriptive error messages that try to help you not only spot the error but also will provide a suggestion on how to fix the bug.
If make runs successfully, you will see three warning messages:
lab_intro.cpp:57:36: warning: unused parameter 'centerX' [-Wunused-parameter]
PNG createSpotlight(PNG image, int centerX, int centerY) {
^
lab_intro.cpp:57:49: warning: unused parameter 'centerY' [-Wunused-parameter]
PNG createSpotlight(PNG image, int centerX, int centerY) {
^
lab_intro.cpp:91:35: warning: unused parameter 'secondImage'
[-Wunused-parameter]
PNG watermark(PNG firstImage, PNG secondImage) {
^
This is expected – you have not written these functions yet.
CS 225’s PNG Class
Inside of your cs225 directory, you may have noticed PNG.h and PNG.cpp. We have provided an already complete PNG class that saves and loads PNG files and exposes a simple API for you to modify PNG files.
In C++, the scope resolution operator, ::, denotes a function or variable is a member of a class. The API for the PNG class includes:
- Loading/Saving PNG files:
bool PNG::readFromFile(const std::string & fileName), loads an image based on the provided file namebool PNG::writeToFile(const std::string & fileName), writes the current image to the provided file name (overwriting existing files)
- Retrieving image and pixel information:
unsigned int PNG::width() const, returns the width of the imageunsigned int PNG::height() const, returns the height of the imageHSLAPixel & getPixel(unsigned int x, unsigned int y), returns a pointer to a pixel at a provided location
- Methods to create empty PNGs, resizing an image, etc.
Open the doxygen for PNG
Example Usage
Suppose we want to transform an image to grayscale. Earlier you learned that a pixel with a saturation set to 0% will be a gray pixel. For example, here’s this transformation applied to the Alma Mater:
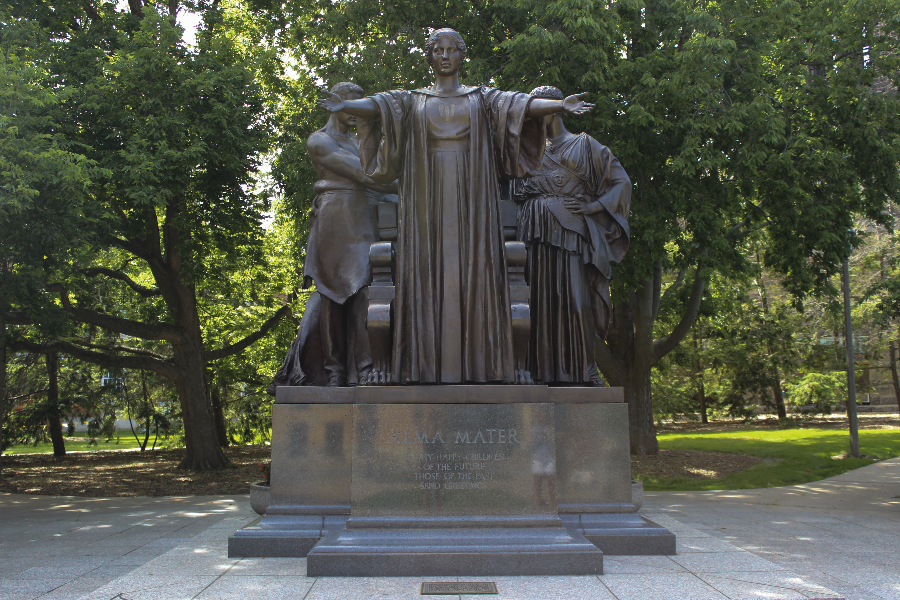 alma.png
alma.png
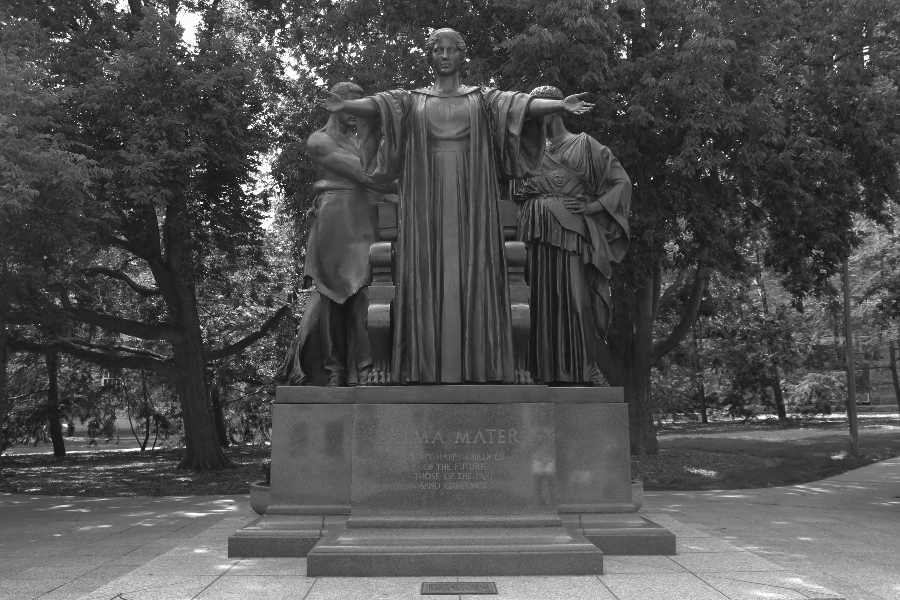 out-grayscale.png
out-grayscale.png
The code that was used to create the above image follows:
// Function `grayscale` receives a PNG as input by reference
void grayscale(PNG & png) {
// Loop through all of pixels of the PNG (width x height):
for (unsigned int x = 0; x < png.width(); x++) {
for (unsigned int y = 0; y < png.height(); y++) {
// Get a reference to the pixel at (x, y):
HSLAPixel & pixel = png.getPixel(x, y);
// Set the pixel's saturation to 0:
pixel.s = 0;
// ...that's it! Since `pixel` is a reference, the memory storing the pixel
// is the memory inside of the PNG image. No need to `set` the pixel.
}
}
}
Lab Assignment: Modify the PNG in three new ways!
To complete the lab, complete illinify, spotlight, and watermark functions in lab_intro.cpp. You will find a complete grayscale function (above) is already provided for you.
All C++ programs begin with the main function, which is usually defined in main.cpp. You can find that a main function has been provided for you that:
- Loads in the image
alma.png - Calls each image modification function
- Saves the modified image as
out-MODIFIED.png, whereMODIFIEDis the modification (eg:out-grayscale.png)
A description of each function is provided in lab_intro.cpp and examples are given below:
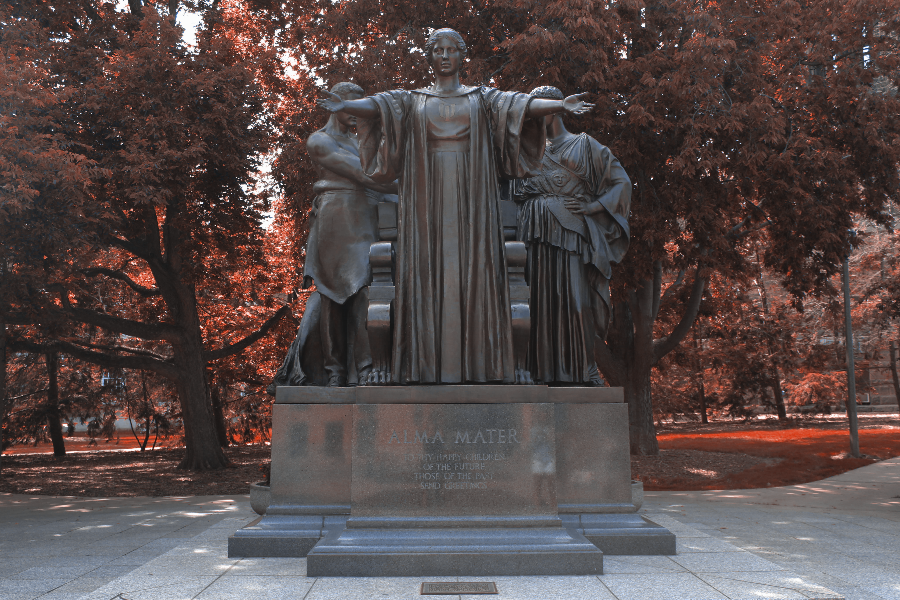

To illinify an image is to transform the hue of every pixel to Illini Orange or Illini Blue.
The hue of every pixel is set to the a hue value of either orange or blue, based on if the pixel’s hue value is closer to orange than blue. Remember, hue values are a circle!

To spotlight an image is to create a spotlight centered at a given point: (centerX, centerY).
A spotlight adjusts the luminance of a pixel based on the Euclidean distance the pixel is away from the center by decreasing the luminance by 0.5% per 1 pixel Euclidean distance away from the center, up to an 80% decrease in luminance.
For example, a pixel 3 pixels above and 4 pixels to the right of the center is a total of pixels away and its luminance is decreased by 2.5% (0.975x its original value). At a distance over 160 pixels away, the luminance will always be decreased by 80% (0.2x its original value).

To watermark an image is to lighten a region of an image based on the contents of a spotlight, given both images.
For every pixel that exists within the bounds of both image and spotlight, the luminance of image must be increased by +0.2 (absolute, but not to exceed 1.0) if and only if the luminance of spotlight at the same pixel is 100%.
You should not assume anything about the size of the images. However, you need only consider the range of pixels that exist in both images.
Compiling the Code
To compile your code, run the following from your lab_intro directory:
$ make
Running Your Code
If your code compiled without errors, an executable named lab_intro will be built. This executable starts by running the main function, which calls each of your image manipulation functions. Run it by running:
$ ./lab_intro
Check out out-illinify.png and see what your code did!
Testing Your Code
In CS 225, we use the widely-used C++ testing framework catch. Unit tests are provided for you in the tests folder and catch will run each of the unit tests for you. You are always encouraged to write additional test cases.
To make the test suite, run:
$ make test
After compiling the test suite, run the tests using:
$ ./test
For more information on running tests with Catch and interpreting the results, see Testing with Catch.
Submitting Your Work
You must submit your work on Prairielearn for grading. We will use the following files for grading:
lab_intro.cpp
All other files will be ignored in grading.