Andrew Samboy (asamboy2, ECE120), Ningdong Wang (nw3, ECE110), and Moriah Gau (mgau2, ECE110)
Introduction:
When was the last time you lost the TV remote with no hope of finding it? In a world where technology is growing increasingly small and mobile, the unfortunate many who have experienced the loss of any personal devices are more than familiar with the pain of experiencing such an incident. You no longer have to spend hours and days searching for your lost device, for the Indoor Positioning System allows the owner to scan any room for said device in a fast and efficient manner.
Background Research:
People are losing their possessions everyday. Even when you think it's in your hand, the next second it's gone and you spend hours searching for it but it just refuses to be found. According to Mozy (by Dell), the average person loses about 1.24 items a year and most of it is never recovered. The average cost of a lost item is $220.15! As technology continues to develop more innovations are being made; inventions such as Tiles are allowing people to access the locations of their lost items via Bluetooth in new ways that were never thought possible. However, along with these cool functions also comes lots of money; thus, the indoor positioning system seeks to be convenient yet affordable deivice that can help its users save both their time and money.
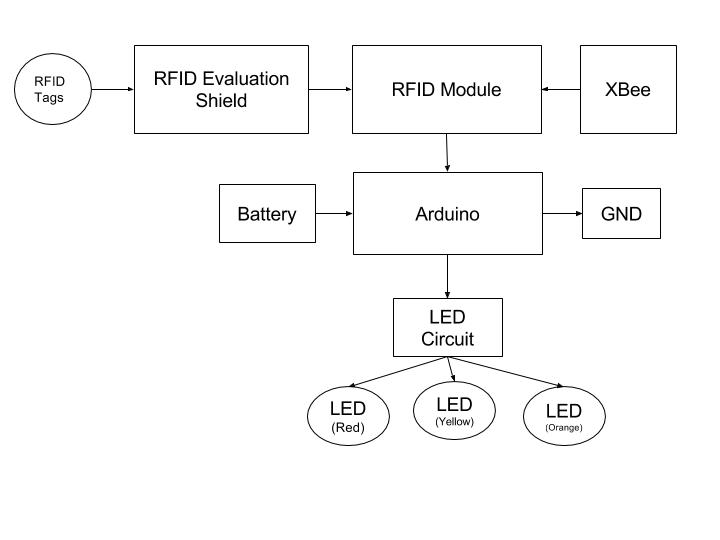
Block Diagram:
System Overview:
The user must manually scans the room with the Indoor Positioning System. The RFID receiver encased in a housing of the Indoor Positioning System would act similarly to a metal detector and alert the user immediately when the missing object is in range of the receiver. The RFID Evaluation Shield, that has its inputs connected to the inputs of the Arduino, would detect the presence of the RFID tags if they are within its detection parameters and would send a signal input to the RFID Module and send another individualized input to the Arduino board based on the ID code of the RFID tag. Based on the the input received from the RFID Module, the Arduino runs through the code converts the ID of the RFID tag to HEX and displays it on the screen and the colored LED that were assigned by the user for different objects (remotes, keys, phones, etc) will light up accordingly.
Required Parts:
- RFID Tags
- RFID Module (SM130 MIFARE)
- RFID Evaluation Shield
- XBee Wifi Module
- Battery
- LEDs
- Arduino
- Breadboards
- Jumper Wires
- Headers
Possible Challenges:
i. Attaining an effective proximity range
ii. Mobility and Size
iii. Programming with Arduino
iv. Occasional Error with RFID Reading Output on Arduino
FINAL LAB REPORT:
Resources:
https://mozy.com/about/news/reports/lost-and-found/
http://www.tigoe.com/pcomp/code/PHP/347/
https://github.com/sparkfun/RFID_Evaluation_Shield/blob/master/Firmware/RFID_Eval_13_56MHz.ino